Preventive Healthcare for Seniors A Comprehensive Guide
Preventive healthcare for seniors is paramount for maintaining quality of life and extending healthy lifespan. This guide delves into the crucial aspects of proactive health management for older adults, addressing common health concerns, preventative strategies, and the role of lifestyle choices. We’ll explore how nutrition, exercise, mental well-being, and technological advancements contribute to a holistic approach to senior wellness, empowering individuals to age actively and vibrantly.
Understanding the unique health challenges faced by seniors, such as increased risk of chronic diseases and age-related physical changes, is critical. This guide provides practical advice and resources to help seniors and their caregivers navigate these challenges effectively, promoting independence and overall well-being. We will examine various strategies for disease prevention, health screenings, and the importance of maintaining a healthy lifestyle through diet, exercise, and stress management.
Defining Preventive Healthcare for Seniors
Preventive healthcare for seniors focuses on proactive strategies to maintain health, prevent disease, and manage existing conditions, thereby enhancing quality of life and independence. It’s a crucial aspect of geriatric care, shifting the emphasis from treating illness to preventing its onset or slowing its progression. This approach significantly impacts both the individual’s well-being and the overall healthcare system’s efficiency.Preventive healthcare for seniors encompasses a range of services designed to address the unique health challenges faced by older adults.
These services are tailored to the physiological changes associated with aging and the increased risk of chronic diseases common in this population. Unlike younger adults who may focus primarily on injury prevention and addressing acute illnesses, seniors require a more comprehensive approach encompassing disease management, early detection, and lifestyle modifications.
Core Components of Preventive Healthcare for Seniors
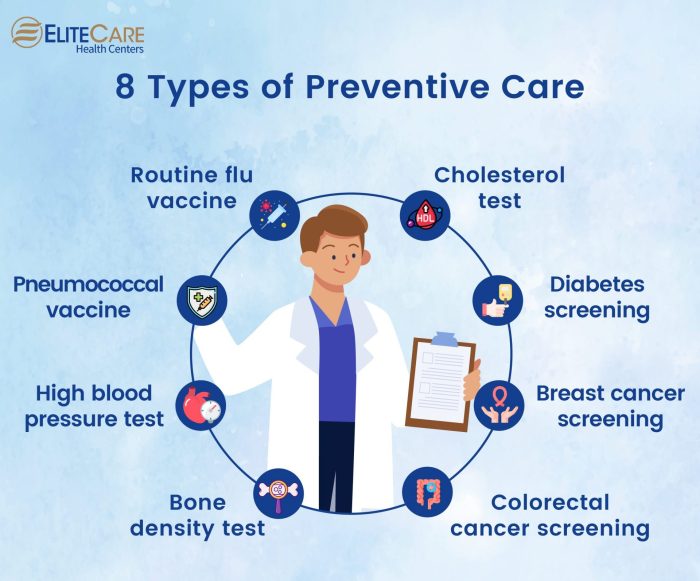
Preventive healthcare for seniors involves several key components working in concert. These include regular health screenings (blood pressure, cholesterol, blood sugar), vaccinations (flu, pneumonia, shingles), healthy lifestyle counseling (diet, exercise, smoking cessation), and medication management to prevent adverse drug events and ensure optimal effectiveness. Furthermore, regular check-ups with a physician or geriatric specialist are essential to monitor overall health and address any emerging concerns promptly.
Mental health screenings and support are also vital components, given the increased risk of depression and anxiety among seniors. Finally, attention to safety measures within the home environment can prevent falls and other accidents, contributing significantly to overall well-being and independence.
Differences Between Preventive Care for Seniors and Younger Adults
The primary difference lies in the focus and scope of preventive measures. While younger adults often concentrate on injury prevention and addressing acute illnesses, preventive care for seniors emphasizes the management and prevention of chronic diseases like heart disease, diabetes, and arthritis. The frequency of screenings and check-ups is also higher for seniors due to the increased likelihood of developing age-related conditions.
Furthermore, the preventive strategies for seniors often incorporate a stronger emphasis on medication management, fall prevention, and addressing age-related cognitive decline. For example, a young adult might focus on regular exercise to maintain fitness, while a senior might incorporate exercises designed to improve balance and strength to reduce the risk of falls.
Common Health Concerns Requiring Proactive Attention in Seniors
The following table Artikels common health concerns that require proactive attention in seniors:
| Cardiovascular Health | Cognitive Health | Musculoskeletal Health | Vision and Hearing |
|---|---|---|---|
| High blood pressure High cholesterol Heart disease |
Dementia Alzheimer’s disease Cognitive decline |
Osteoporosis Osteoarthritis Falls |
Macular degeneration Cataracts Hearing loss |
Common Health Risks and Prevention Strategies
Maintaining good health in later life is a significant concern, and proactive preventive healthcare plays a crucial role in ensuring a higher quality of life for seniors. Understanding common health risks and implementing appropriate prevention strategies is key to mitigating potential health issues and promoting longevity. This section will explore common health risks among seniors and Artikel practical preventive measures.Preventive healthcare for seniors focuses on identifying and managing potential health problems before they become serious.
This approach significantly improves the likelihood of a healthy and independent life. By addressing risk factors early, seniors can reduce their chances of developing chronic diseases and maintain their overall well-being.
Chronic Disease Risks and Prevention
Chronic diseases, such as heart disease, diabetes, and arthritis, are significantly more prevalent among older adults. Heart disease, often linked to high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and unhealthy lifestyle choices, can lead to heart attacks and strokes. Diabetes, characterized by high blood sugar levels, increases the risk of complications affecting the eyes, kidneys, and nerves. Arthritis, encompassing various joint conditions, causes pain, stiffness, and reduced mobility.
Fortunately, many of these conditions are preventable or manageable through lifestyle changes and regular medical check-ups. For example, maintaining a healthy weight, following a balanced diet, engaging in regular physical activity, and avoiding smoking significantly reduces the risk of developing heart disease and type 2 diabetes. Similarly, managing weight, maintaining a healthy diet, and performing regular low-impact exercises can help manage arthritis symptoms.
Importance and Frequency of Regular Health Screenings
Regular health screenings are vital for early detection and management of potential health problems. These screenings allow healthcare professionals to identify diseases or conditions in their early stages, often before symptoms appear, facilitating timely intervention and improved outcomes. Blood pressure checks should be performed regularly, ideally at least annually, or more frequently depending on individual risk factors and existing conditions.
Cholesterol screenings are recommended periodically, usually every few years, to monitor cholesterol levels and assess the risk of heart disease. Cancer screenings, such as mammograms for breast cancer, colonoscopies for colorectal cancer, and prostate-specific antigen (PSA) tests for prostate cancer, are crucial for early detection and treatment, with recommended frequencies varying depending on age, family history, and other risk factors.
The specific recommendations for screening frequencies should be discussed with a healthcare provider.
Lifestyle Modifications to Mitigate Health Risks
Adopting healthy lifestyle changes can significantly reduce the risk of developing chronic diseases and improve overall well-being in seniors. The following table categorizes lifestyle modifications based on their impact on different aspects of health:
| Lifestyle Modification | Impact on Health |
|---|---|
| Balanced Diet (rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean protein) | Cardiovascular Health, Weight Management, Diabetes Prevention |
| Regular Physical Activity (at least 30 minutes most days of the week) | Cardiovascular Health, Weight Management, Bone Health, Mental Well-being |
| Adequate Sleep (7-8 hours per night) | Mental Well-being, Immune Function, Cardiovascular Health |
| Stress Management Techniques (yoga, meditation, deep breathing) | Mental Well-being, Cardiovascular Health, Immune Function |
| Social Engagement (maintaining strong social connections) | Mental Well-being, Cognitive Function |
| Smoking Cessation | Cardiovascular Health, Respiratory Health, Cancer Prevention |
| Limited Alcohol Consumption | Cardiovascular Health, Liver Health |
Nutrition and Diet for Senior Wellness
Maintaining a healthy diet is crucial for seniors to support their overall well-being and manage age-related health challenges. Proper nutrition helps maintain energy levels, strengthens the immune system, and reduces the risk of chronic diseases. A balanced diet rich in essential nutrients plays a vital role in preserving bone density, cognitive function, and overall physical health during the aging process.
Dietary needs change as we age. Many seniors experience decreased appetite, difficulty chewing or swallowing, and changes in taste and smell, impacting their nutritional intake. Therefore, understanding these changes and adapting dietary strategies is essential for promoting optimal health and preventing malnutrition.
Sample Weekly Meal Plan
This sample meal plan emphasizes nutrient-rich foods beneficial for senior health. It focuses on easily digestible foods and considers common dietary challenges faced by seniors. Remember to consult with a doctor or registered dietitian to personalize a plan based on individual needs and health conditions.
| Day | Breakfast | Lunch | Dinner |
|---|---|---|---|
| Monday | Oatmeal with berries and nuts | Chicken salad sandwich on whole-wheat bread with a side salad | Baked salmon with roasted vegetables |
| Tuesday | Scrambled eggs with spinach and whole-wheat toast | Lentil soup with a whole-grain roll | Lean ground beef stir-fry with brown rice |
| Wednesday | Yogurt with granola and fruit | Tuna salad with avocado on whole-wheat crackers | Chicken breast with sweet potato and green beans |
| Thursday | Whole-wheat pancakes with fruit and syrup | Leftover chicken breast with a side salad | Vegetarian chili with cornbread |
| Friday | Breakfast burrito with eggs, beans, and salsa | Turkey and cheese sandwich on whole-wheat bread with tomato soup | Pasta with marinara sauce and meatballs |
| Saturday | French toast with berries | Leftover pasta | Roast chicken with mashed potatoes and gravy |
| Sunday | Waffles with fruit and whipped cream | Salad with grilled chicken or fish | Pork tenderloin with roasted vegetables |
Managing Common Dietary Challenges
Addressing common dietary challenges is crucial for ensuring adequate nutrient intake among seniors. Several strategies can help overcome these obstacles and maintain a healthy diet.
For difficulty swallowing (dysphagia), soft, pureed, or easily chewed foods are recommended. Consider using thickening agents for liquids. Smaller, more frequent meals can also be easier to manage. For decreased appetite, making meals appealing visually and aromatically can help stimulate appetite. Offering a variety of flavors and textures can also increase food intake.
In cases of significant appetite loss, consulting a doctor or dietitian is essential to rule out underlying medical conditions.
Role of Vitamins and Minerals in Senior Health
Specific vitamins and minerals play crucial roles in maintaining the health and well-being of seniors. Adequate intake is essential for preventing deficiencies and supporting various bodily functions.
| Vitamin/Mineral | Role in Senior Health | Food Sources |
|---|---|---|
| Calcium | Essential for maintaining bone health and preventing osteoporosis. Supports muscle function and nerve transmission. | Dairy products (milk, yogurt, cheese), leafy green vegetables (kale, spinach), fortified foods (cereals, juices) |
| Vitamin D | Crucial for calcium absorption and bone health. Plays a role in immune function and muscle strength. Many seniors are deficient, so supplementation may be necessary. | Fatty fish (salmon, tuna), egg yolks, fortified foods (milk, cereals), sunlight exposure |
| B Vitamins (B1, B6, B12) | Essential for energy production, nerve function, and red blood cell formation. Deficiencies can lead to fatigue, anemia, and neurological problems. | B1: Whole grains, legumes, pork. B6: Chicken, fish, bananas. B12: Meat, poultry, fish, dairy products, fortified cereals. |
Physical Activity and Exercise Recommendations

Maintaining physical activity is crucial for seniors to preserve their health, independence, and overall quality of life. Regular exercise helps combat age-related decline in muscle mass, bone density, and cardiovascular function, while also improving balance and reducing the risk of falls. The key is to find activities that are enjoyable and tailored to individual abilities and limitations.Regular exercise offers numerous benefits for seniors.
It significantly reduces the risk of chronic diseases like heart disease, stroke, type 2 diabetes, and certain cancers. Furthermore, exercise improves mood, reduces stress and anxiety, and enhances cognitive function, contributing to better mental well-being. Even moderate activity can yield substantial health improvements.
Age-Appropriate Exercises for Seniors with Varying Mobility
Choosing the right type and intensity of exercise is paramount. For those with limited mobility, chair exercises or water aerobics offer low-impact options. More mobile seniors can engage in brisk walking, cycling, or dancing. The focus should always be on gradual progression and listening to the body. It’s beneficial to consult a physician or physical therapist before starting any new exercise program.
- Low Mobility: Chair exercises focusing on arm and leg movements, seated stretches, and gentle range-of-motion activities. These can be performed independently or with assistance.
- Moderate Mobility: Brisk walking, swimming, water aerobics, cycling (stationary or outdoor), and tai chi. These activities improve cardiovascular health and flexibility.
- High Mobility: More vigorous activities like hiking, jogging (if appropriate), dancing, and team sports (adapted to senior capabilities). These activities provide a more intense workout.
Benefits of Different Exercise Types
Different types of exercise offer unique benefits. Strength training helps maintain muscle mass and bone density, combating age-related muscle loss (sarcopenia) and osteoporosis. Cardiovascular exercise improves heart health, lung function, and stamina. Flexibility exercises enhance range of motion, balance, and reduce the risk of falls. A well-rounded exercise program incorporates all three.
- Strength Training: Using resistance bands, light weights, or bodyweight exercises strengthens muscles, improving balance and reducing the risk of falls. Examples include chair squats, wall push-ups, and bicep curls with resistance bands.
- Cardiovascular Exercise: Activities that raise the heart rate and improve cardiovascular fitness, such as brisk walking, swimming, or cycling. These exercises improve heart and lung health and increase stamina.
- Flexibility Exercises: Stretching exercises that improve range of motion and flexibility, reducing stiffness and the risk of injury. Examples include gentle yoga, tai chi, and simple stretches like reaching for toes or extending arms overhead.
Sample Low-Impact Exercise Routine, Preventive healthcare for seniors
This routine can be adapted to individual fitness levels and limitations. Remember to consult your doctor before starting any new exercise program.
Warm-up (5 minutes): Gentle range-of-motion exercises for all major joints, such as arm circles, leg swings, and neck rotations. Imagine slowly moving each joint through its full range of motion without any strain.
Strength Training (10 minutes):
- Chair Stands (10 repetitions): Stand up from a chair slowly and carefully, then sit back down. Focus on using your leg muscles to perform this movement.
- Wall Push-ups (10 repetitions): Lean against a wall with your hands shoulder-width apart. Slowly bend your elbows, lowering your chest towards the wall, and then push back up.
- Resistance Band Bicep Curls (10 repetitions each arm): Hold a resistance band with both hands, keeping your elbows close to your sides. Curl the band towards your shoulders, squeezing your biceps at the top. Slowly lower the band back down.
Cardiovascular Exercise (15 minutes): Brisk walking at a comfortable pace. This could be done indoors or outdoors, depending on weather and mobility. Maintain a pace that slightly elevates your heart rate but allows you to hold a conversation.
Flexibility Exercises (5 minutes): Gentle stretches, such as neck stretches, shoulder stretches, and hamstring stretches. Hold each stretch for 15-30 seconds, breathing deeply throughout.
Cool-down (5 minutes): Slow walking and gentle stretching. This helps your body gradually return to its resting state.
By embracing a proactive and holistic approach to preventive healthcare, seniors can significantly improve their quality of life and enjoy a healthier, more fulfilling later life. This guide has highlighted the importance of regular health screenings, lifestyle modifications, and the utilization of available resources and support networks. Remember, proactive healthcare is an investment in longevity and well-being—a journey towards a healthier and happier future.
FAQ Corner: Preventive Healthcare For Seniors
What are the most common age-related health issues?
Common issues include heart disease, stroke, arthritis, osteoporosis, diabetes, and cognitive decline.
How often should seniors have health checkups?
Frequency varies based on individual health and risk factors, but annual checkups are generally recommended, with more frequent visits as needed.
Are there financial assistance programs for senior healthcare?
Yes, many government and private programs offer financial assistance for healthcare costs. Consult local resources or social workers for more information.
What if I can’t afford preventative care?
Explore options such as community health clinics, government assistance programs (Medicaid/Medicare), and charitable organizations offering subsidized or free services.



